First of all the NITI stands for National Institution for Transforming India. It is a non- constitutional body established on
January 1, 2015 replacing age-old, planning commission of India.
NITI Aayog is a think tank (or
an advice and planning committee) of Government of India formed mainly to
provide both directional and policy inputs. This has been framed by scraping
out the ‘Planning commission’, which used to make 5 years plans and
distribution of finance for various state and central plans. Being an advisory committee, while designing strategic and long term policies and programmes for the Government of India, NITI Aayog also provides relevant technical advice to the Centre and States. The first meeting of NITI Aayog was held on February 8, 2015.
Most of us will have a common
question ie. Is NITI Aayog a constitutional body?, as mentioned earlier NITI
Aayog is neither a constitutional body nor a statutory body, It is Non-
constitutional body/non- statutory with structure as explained below.
Quick facts, before moving further:All government bodies are divided into three types. those are,1.Constitutional body: Any government body or organization which has been created after its mention in constitution and it is most important body among all. example: election commission of India 2.Statutory body: any body which has been formed after an act/law has been passed by the parliament/assembly. example: SEBI(Securities and Exchange Board of India) 3.Non-constitutional: any and non- statuary body which has been formed by the government with an agenda to fulfill and for ease of governing, generally these bodies will be converted into statutory. example: NITI Aayog |
Body and Members of NITI Aayog:
Unlike Planning commission NITI Aayog is a body with bottom up approach in advisory method. Whre the planning ideas and suggestions comes from lower most elements of the body. The Headquarter of Aayog is at Delhi with Prime minister being chairperson of the body. The prime minister himself choses other parts of this organization.
Chief ministers of all states/Delhi/Puduchery and Lt. governors of union territories are permanent members of the commission and this is also governing and regional council of the body. Temporary members are generally chosen from various leading universities and research institutes of the country.
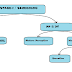
For easy understanding the structure is schematically explained below,
For easy understanding the structure is schematically explained below,
 |
| NITI Aayog structure |
Current body constitutes of,
| POST | PERSON |
| Chairperson |
Shri Narendra Modi, Hon'ble Prime Minister
|
| Vice Chairperson |
Dr. Rajiv Kumar
|
| CEO |
Shri Amitabh Kant
|
| Full-Time Members |
(i) Shri V.K. Saraswat
(ii) Prof. Ramesh Chand (iii) Dr. V. K. Paul |
| Ex-officio Members |
(i) Shri Raj Nath Singh, Minister of Defence
(ii) Shri Amit Shah, Minister of Home Affairs
(iii) Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, Minister of Finance and Minister of Corporate Affairs
(iv) Shri Narendra Singh Tomar, Minister of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare;Minister of Rural Development; Minister of Panchayati Raj.
|
| Special Invitees |
(i) Shri Nitin Jairam Gadkari, Minister of Road Transport and Highways; Minister of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
(ii) ShriThaawar Chand Gehlot, Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment.
(iii) Shri Piyush Goyal, Minister of Railways; and Minister of Commerce and Industry
(iv) Shri Rao Inderjit Singh, Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation and Minister of State(Independent Charge) of Ministry of Planning.
|
| Permanent members | Chief ministers of all states/Delhi/Puduchery and Lt. governors of union territories. |
Besides all other structures, There are mainly two types of Hubs in NITI Aayog, those are,
1) Team India Hub: which mainly engages states with center.
2) Knowledge and Innovation Hub: this forms the main think tank of the commission.
The detailed functions of NITI Ayog are given below
Functions of NITI Aayog:
The NITI Aayog is mainly an advisory committee which does not hold any financial decision making /distribution power. As mentioned earlier, unlike Planning commission of India, the NITI Aayog follows bottom up approach for its discussions hence it emphasizes state's involvement in it. "Collaboration of center with states in planning" would be right words to use here.
The following are main functions of it.
1. Prioritizing shared sectors and strategies with active participation of states.
2. To foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the States on a continuous basis, recognizing that strong States make a strong nation.
3. Planning to development of village and lower level to empower it for its active participation in future decisions.
4. To ensure, on areas that are specifically referred to it, that the interests of national security are incorporated in economic strategy and policy.
5. To pay special attention to the sections of our society that may be at risk of not benefiting adequately from economic progress.
6. To make long term plans and involving feedback collection of it, mainly to innovate it, if there is scope to do so.
7. To provide advice and encourage partnerships between key stakeholders and national and international like-minded Think tanks, as well as educational and policy research institutions.
8. To create a knowledge, innovation and entrepreneurial support system through a collaborative community of national and international experts, practitioners and other partners.
9. It is also frames a platform to resolve inter-sectoral and inter departmental issues to accelerate development and growth of the nation.
10. To maintain a 'state-of-the-art' Resource Center, be a repository of research on good governance and best practices in sustainable and equitable development as well as help their dissemination to stake-holders.
11. To actively monitor and evaluate the implementation of programmes and initiatives, including the identification of the needed resources so as to strengthen the probability of success and scope of delivery.
12.Mainly it has vision to support and plan the technology upgrading plans of the country.
13. To undertake other activities as may be necessary in order to further the execution of the national development agenda, and the objectives mentioned above.
The following are main functions of it.
1. Prioritizing shared sectors and strategies with active participation of states.
2. To foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the States on a continuous basis, recognizing that strong States make a strong nation.
3. Planning to development of village and lower level to empower it for its active participation in future decisions.
4. To ensure, on areas that are specifically referred to it, that the interests of national security are incorporated in economic strategy and policy.
5. To pay special attention to the sections of our society that may be at risk of not benefiting adequately from economic progress.
6. To make long term plans and involving feedback collection of it, mainly to innovate it, if there is scope to do so.
7. To provide advice and encourage partnerships between key stakeholders and national and international like-minded Think tanks, as well as educational and policy research institutions.
8. To create a knowledge, innovation and entrepreneurial support system through a collaborative community of national and international experts, practitioners and other partners.
9. It is also frames a platform to resolve inter-sectoral and inter departmental issues to accelerate development and growth of the nation.
10. To maintain a 'state-of-the-art' Resource Center, be a repository of research on good governance and best practices in sustainable and equitable development as well as help their dissemination to stake-holders.
11. To actively monitor and evaluate the implementation of programmes and initiatives, including the identification of the needed resources so as to strengthen the probability of success and scope of delivery.
12.Mainly it has vision to support and plan the technology upgrading plans of the country.
13. To undertake other activities as may be necessary in order to further the execution of the national development agenda, and the objectives mentioned above.
How NITI Aayog is different from planning commission?
Most of you might have got a question like, if the NITI Aayog replaced the Planning commission what are the major difference between them?Planning Commission follows top down model while NITI Aayog follows bottom up approach.
Unlike Planning Commission it is only a advisory committee and it does not make any financial division and most importantly five years plan scheme being cut down from PC (last five years plan was from 2012-17)
Quick facts, before moving further:Planning Commission:Planning commision famously known as 'Yojana Aayog' was a commision mainly formed, concentrating on developement of the country in various sectors. It was established on 15th March 1950 by Prime minister Jawahar Lal Nehru. This commission is being mainly known for one of its functioning that is 'Five year Plan'. The '12th five years plan(2012 - 2017)' was last of it. It was scrapped in 2014 by NDA government to form NITI Aayog. It was considerably quite successful body with emphasis on social reforms. To read more about it click HERE |
If you have any query/ feedback/ suggestions, please feel free to comment down below.